MYOFASCIAL RELEASE
Myofascial Release (MFR) is a holistic, therapeutic approach to manual therapy. MFR offers a comprehensive approach for the evaluation and treatment of the myofascial system, the system of tissues and muscles in the body.
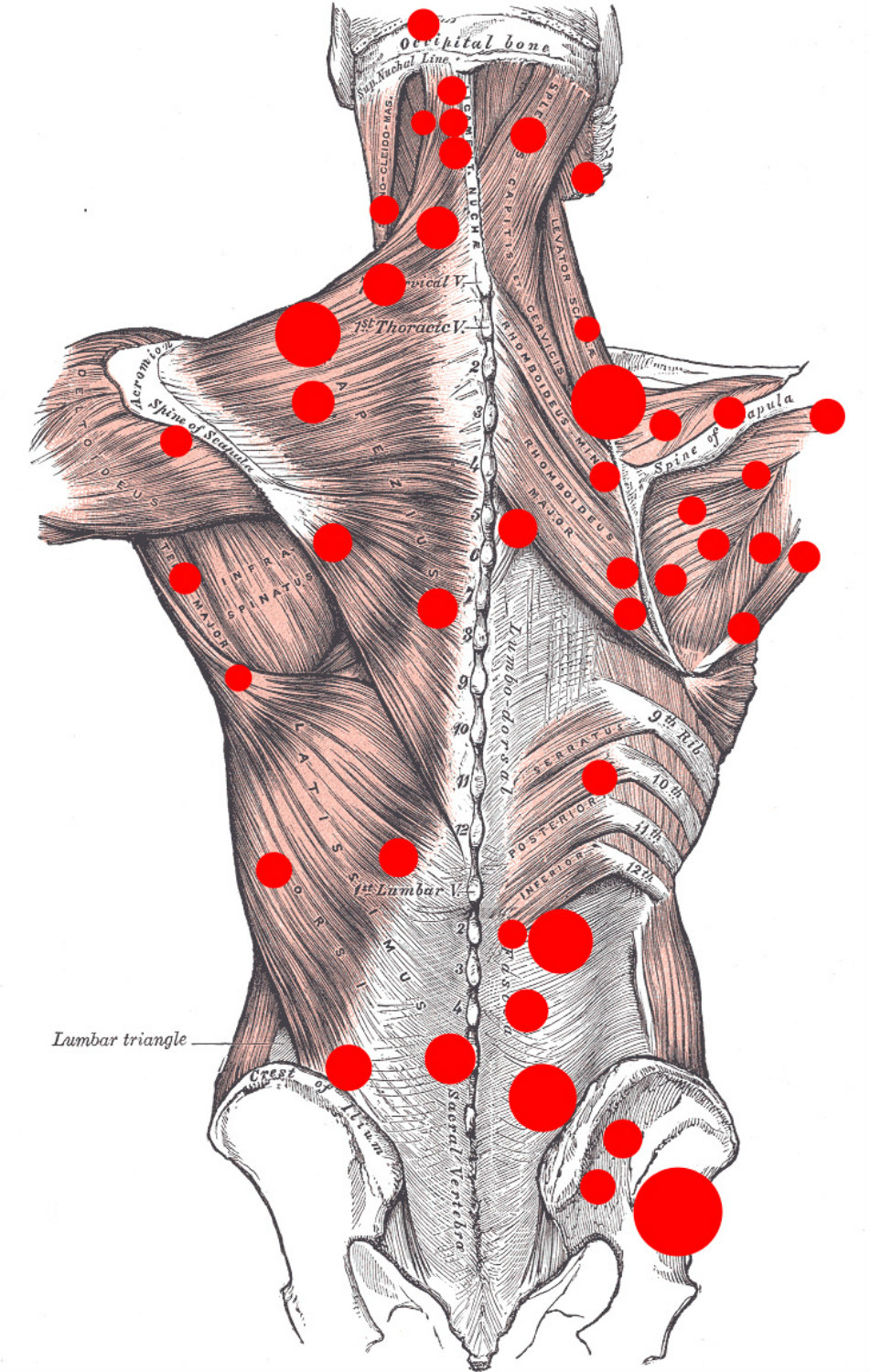
This technique is designed to release restrictions such a trigger points, muscle tightness, and dysfunctions in soft tissue that may cause pain and limit motion in all parts of the body. It has shown success in decreasing pain and increasing mobility. (1)
The main tissue that MFR focuses on for release in the myofascial system is the fascia. Fascia is a fine tissue that surrounds all structures in the body including muscles, nerves, vessels, and bones. MFR allows the therapist to evaluate, identify, and treat fascial restrictions. These restrictions can be caused by numerous factors, such as trauma, musculoskeletal conditions, repetitive stress syndrome, and poor posture.
By applying gentle, hands-on techniques to the whole body, positive structural changes may occur, such as increased range of motion, decreased pain, and, most importantly, increased fascial mobility. (2) In combination with traditional physical therapy, MFR can help patients return to their daily and recreational activities.
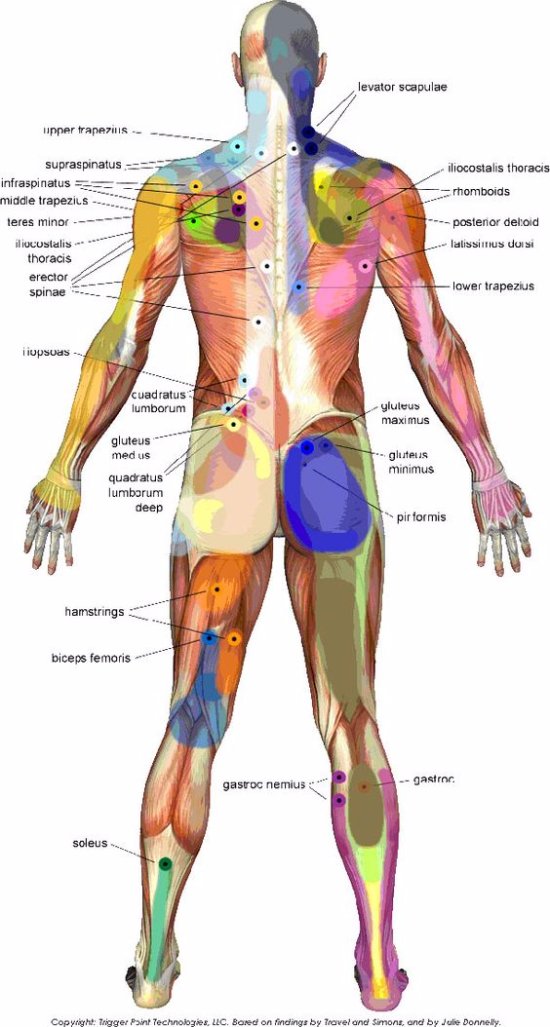
MFR can be used to treat pain and increase mobility in patients with a wide range of conditions, including back pain, neck pain, and fibromyalgia.
Athletes can also benefit. A number of sports injuries can be treated with MFR, including:
- Repetitive strain injuries, often seen in long distance runners
- Muscular imbalances, which lead to overuse in isolated joints and faulty movement patterns
MFR can be used to treat pain and increase mobility in patients with a wide range of conditions, including
- back pain
- neck pain
- fibromyalgia
Athletes can also benefit. A number of sports injuries can be treated with MFR, including:
- Repetitive strain injuries, often seen in long distance runners
- Muscular imbalances, which lead to overuse in isolated joints and faulty movement patterns